In Harvesting the Chemical Energy of the Molecules in Food
The process of harvesting chemical energy from food molecules is fundamental to the survival and function of living organisms. By breaking down macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids through intricate biochemical pathways, cells convert these nutrients into usable energy in the form of ATP. However, the efficiency of this energy conversion is not solely dependent on the macromolecules themselves; it also hinges on the presence of essential nutrients that facilitate enzymatic reactions. In Harvesting the Chemical Energy of the Molecules in FoodUnderstanding this intricate interplay raises critical questions about nutritional adequacy and its implications for energy metabolism in various contexts.
Understanding Chemical Energy
Chemical energy, a fundamental concept in biochemistry, refers to the energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds, particularly in organic molecules derived from food.
This energy is released during metabolic processes through energy transfer, governed by thermodynamic principles. The breaking and forming of chemical bonds during molecular interactions facilitate this release, underscoring the intricate balance between energy storage and utilization in biological systems.
The Role of Macromolecules
Macromolecules play a pivotal role in the harvesting of chemical energy from food, acting as the primary substrates for metabolic processes.
Read also Art:0mqfhrsn2tu= Demon Slayer Manga
Protein structures facilitate enzymatic reactions, while carbohydrate functions provide immediate energy sources.
Lipid roles encompass energy storage and membrane integrity, In Harvesting the Chemical Energy of the Molecules in Foodand nucleic acid significance lies in the regulation of metabolic pathways.
Together, these macromolecules orchestrate the efficient utilization of energy from dietary intake.
Biochemical Pathways Explained
The intricate network of biochemical pathways serves as the foundation for energy extraction and utilization within living organisms.
Through various metabolic processes, enzyme function plays a crucial role in energy conversion during cellular respiration. This series of biochemical reactions facilitates nutrient breakdown, ultimately leading to ATP production.
The efficiency of these pathways significantly influences energy yieldIn Harvesting the Chemical Energy of the Molecules in Food, highlighting their importance in sustaining life and promoting cellular activities.
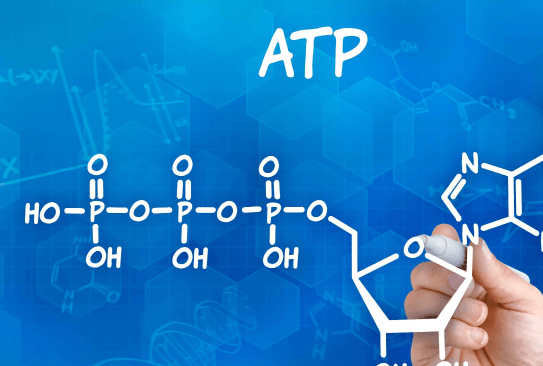
Nutrient Importance in Energy Harvesting
A diverse array of nutrients plays a pivotal role in the effective harvesting of energy from food, each contributing unique properties essential for metabolic processes.
Vitamin significance is underscored by their roles as coenzymes, facilitating enzymatic reactions.
Read also Art:2axccfkd-La= Archangel Michael
Meanwhile, mineral contributions are critical for maintaining cellular functions and energy transfer, ensuring optimal biochemical pathways operate efficiently, In Harvesting the Chemical Energy of the Molecules in Foodultimately enhancing the body’s capacity to extract and utilize energy from consumed nutrients.
Conclusion
The intricate process of harvesting chemical energy from food mirrors a finely-tuned orchestra, where each macromolecule plays a distinct instrument in the symphony of cellular respiration. Enzymes, akin to conductors, guide these reactions, ensuring harmony and efficiency in ATP production. However, just as a musician relies on proper training and quality instruments, the efficiency of energy extraction is contingent upon the availability of essential nutrients. Thus, a balanced diet is paramount for optimal metabolic performance and sustaining life.






